La fonction exponentielle
La fonction exponentielle
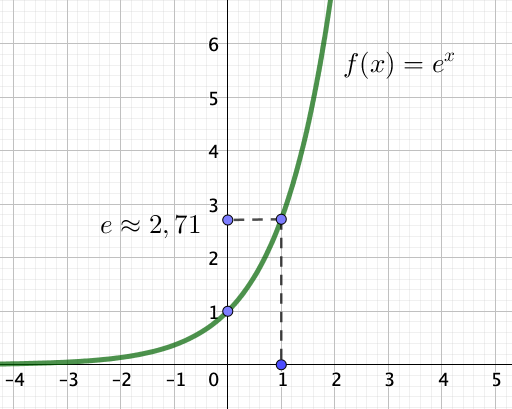
La fonction \(f(x)=exp(x)\) est l’unique fonction définie par :
\(f'(x) = f(x)\)
\(f(0) = 1\)
La fonction exponentielle est continue et dérivable sur \(\mathbb{R}\).
On la note : $exp(x)$= $e^x$
Remarque
Pour tout $x\in \mathbb{R}, e^x>0$
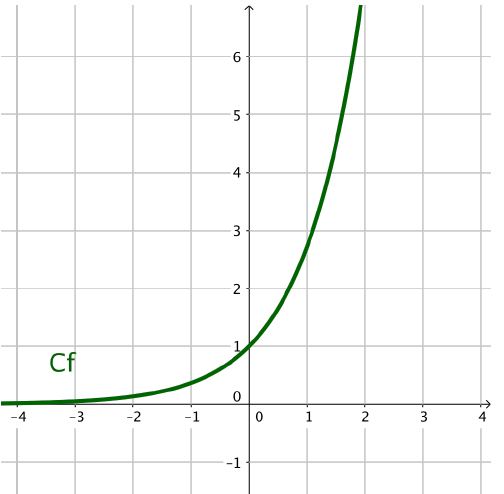
Représentation graphique
Fonctions exponentielles - Propriétés analytiques
Propriétés analytiques
La fonction $e^x$ est définie et dérivable sur $\mathbb{R}$.
Pour tout réel $x$, $(e^x)’= e^x$ et $e^0=1$:
On a aussi :
$e^x>0$
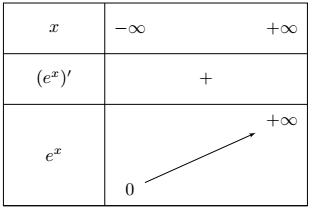
$\lim \limits_{x \rightarrow -\infty} e^x=0$
$\lim \limits_{x \rightarrow +\infty} e^x= +\infty$
$e^1 =e \approx 2,71$
La fonction exponentielle a une dérivée strictement positive donc elle est strictement croissante sur $\mathbb{R}$.
Représentation graphique de la fonction exponentielle
Fonction exponentielle : propriétés algébriques
La fonction exponentielle, propriétés algébriques.
Définition
La fonction \(f(x)=exp(x)\) est l’unique fonction définie par :
\(f'(x) = f(x)\)
\(f(0) = 1\)
La fonction exponentielle est continue et dérivable sur \(\mathbb{R}\).
On la note : $exp(x)$= $e^x$
Propriétés algébriques :
Pour tous réels \(x\) et \(y\)
- \(e^{x+y}=e^x \times e^y\)
- \(e^{-x}=\dfrac{1}{e^x}\)
- \(e^{x-y} = \dfrac{e^x}{e^y}\)
- \((e^x)^n=e^{nx}\) avec n appartenant à \(\mathbb{Z}\)
- Pour tout réel \(x\), \(\ln e^x=x\)
- Pour tout réel \(x>0 \), \(e^{\ln x}=x\)